Gold, often seen as a safe haven asset, has a reputation for being a relatively stable store of value, particularly during times of economic uncertainty. However, despite this, its price can experience significant volatility. Gold’s price fluctuations can be influenced by a range of factors, from global economic events to market speculation, and its volatility can present both opportunities and risks for investors. In this article, we will explore the key factors contributing to gold’s price volatility, provide a detailed analysis of recent fluctuations, and offer insights into how investors can use these fluctuations to their advantage. We will also provide expert predictions for gold’s price volatility in 2025 and beyond.
Factors Contributing to Gold’s Price Volatility
Gold’s price can be highly volatile for a variety of reasons, with both external and internal factors influencing its value. Understanding the drivers behind these fluctuations is crucial for investors looking to navigate the gold market effectively.
1. Global Economic Events
Gold is often seen as a safe-haven asset during times of global economic uncertainty. When economic crises, such as recessions, financial crashes, or political instability, occur, investors flock to gold as a store of value. This demand often drives up the price of gold. However, the reverse can also be true. During periods of economic growth and stability, when investors are more willing to take risks and move into higher-yielding assets, the demand for gold may decrease, leading to price declines.
Recent examples include the financial crisis of 2008, which saw gold prices soar as investors sought refuge from collapsing financial institutions, and the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, which caused a surge in gold prices as uncertainty about the future of global markets increased.
2. Market Speculation
Speculation plays a significant role in gold’s price volatility. Investors and traders in gold futures markets, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and other derivative markets often react to short-term news and sentiment, which can lead to rapid price changes. For example, if there is an expectation of rising inflation or a geopolitical crisis, speculators might drive up the price of gold, even if the actual impact of the event has not yet materialized.
The influence of speculation can lead to gold prices becoming detached from fundamentals, as market sentiment drives prices in the short term. This volatility can create both risks and opportunities for traders looking to capitalize on short-term price movements.
3. Central Bank Policies
Central banks around the world have a significant influence on gold prices. When central banks engage in monetary policies such as lowering interest rates, expanding money supply, or implementing quantitative easing, it can lead to a devaluation of fiat currencies and a subsequent rise in gold prices. Conversely, when central banks raise interest rates or tighten monetary policies, gold prices can fall as the opportunity cost of holding gold increases.
For example, the U.S. Federal Reserve’s decision to raise interest rates to combat inflation could put downward pressure on gold prices, as higher interest rates make other assets more attractive relative to gold. On the other hand, dovish monetary policies, such as the interest rate cuts during the pandemic, typically provide a boost to gold prices.
4. Inflation and Deflation
Inflation is often seen as one of the main drivers behind gold price movements. As inflation erodes the purchasing power of fiat currencies, investors flock to gold as a hedge against inflation. Gold has historically performed well during periods of high inflation, as its value tends to rise in response to the declining value of currency. During deflationary periods, however, the reverse may occur, as lower prices and a stronger currency can reduce demand for gold.
Inflation expectations, particularly in major economies such as the United States and China, have a direct impact on the price of gold. When inflation fears rise, investors often move into gold, driving its price up. On the other hand, during periods of low inflation or deflation, gold may underperform as a hedge.
5. Geopolitical Events and Crises
Gold is often considered a safe-haven asset during times of geopolitical uncertainty. Events such as wars, natural disasters, or political crises can lead to fluctuations in gold prices, as investors seek stability in precious metals. For example, gold prices typically rise during times of military conflict or when tensions between major powers heighten, as seen during the Gulf War or in the lead-up to the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
In addition to wars and conflicts, other geopolitical risks, such as trade disputes, sanctions, and diplomatic tensions, can also influence gold’s price. The market’s reaction to these events is often driven by the uncertainty surrounding the potential economic fallout.
A Detailed Analysis of Recent Fluctuations in Gold Prices
Over the past few years, gold has experienced considerable price fluctuations, influenced by a combination of factors including the COVID-19 pandemic, global inflationary pressures, and shifts in monetary policy. Let’s take a closer look at the key events that have shaped gold’s price movements in recent years.
1. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
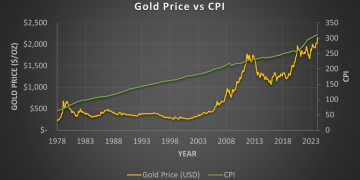
The COVID-19 pandemic created unprecedented levels of economic uncertainty, and gold responded with significant price movements. In the early months of 2020, gold prices surged as investors sought refuge in the metal amid concerns over the global economic downturn. Gold hit an all-time high of over $2,000 per ounce in August 2020 as the economic fallout from the pandemic worsened, central banks implemented massive stimulus packages, and inflation fears began to rise.
However, as vaccine rollouts began and economies started to recover, gold’s price experienced a pullback, dropping below $1,700 per ounce in early 2021. The price fluctuations reflected the changing dynamics of the global economy and investor sentiment.
2. Inflation and Rising Interest Rates in 2021-2022
As the global economy began to recover from the pandemic, inflationary pressures started to build, especially in the U.S. and other major economies. Gold prices briefly surged again in 2022, as inflationary concerns grew. However, as the U.S. Federal Reserve and other central banks raised interest rates to combat rising inflation, gold prices started to experience downward pressure. The expectation of higher interest rates made holding gold, which does not yield interest, less attractive to investors, leading to a decline in gold prices.
Despite these fluctuations, gold remains a popular hedge against inflation, and its performance will continue to be heavily influenced by the central bank policies and inflationary trends in the coming years.

How to Use Price Fluctuations to Your Advantage as an Investor
Gold’s volatility, while sometimes seen as a disadvantage, can actually present opportunities for savvy investors. By understanding the factors that contribute to gold’s price movements, investors can position themselves to benefit from price fluctuations.
1. Buy During Market Dips
One of the most straightforward strategies for investors is to buy gold during price dips. As gold prices are volatile, they often experience periodic corrections, which may present opportunities for investors to purchase gold at a lower price before prices rise again. Investors can use technical analysis and market trends to identify when prices are likely to be at a lower point, providing an entry opportunity for long-term investment.
2. Diversify Your Investment Portfolio
Gold should not be viewed as a standalone investment. While it can act as a safe haven during periods of economic uncertainty, it is also subject to fluctuations that can lead to short-term losses. By diversifying your investment portfolio and including other asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can reduce the risks associated with gold’s price volatility and position yourself for long-term gains.
3. Use Gold as a Hedge Against Inflation
Gold has historically performed well during periods of inflation. By monitoring inflation trends and central bank policies, investors can anticipate periods when gold may rise in value. Allocating a portion of your portfolio to gold can provide a hedge against rising prices and protect your wealth during times of inflation.
4. Monitor Geopolitical Events
As gold prices often react to geopolitical events, investors should stay informed about potential risks in the global landscape. Political instability, wars, and other crises can lead to price spikes, and being prepared for these events can help investors take advantage of sudden market movements.
Predictions for Gold’s Volatility in 2025 and Beyond
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, experts predict that gold’s price volatility will continue to be influenced by a combination of factors, including inflation, interest rates, geopolitical events, and market speculation.
1. Inflation and Central Bank Policies
With inflation still a concern in many major economies, gold is expected to remain a popular hedge against rising prices. Central bank policies will continue to play a major role in determining gold’s price movements, as interest rate changes and quantitative easing can significantly impact investor demand for gold.
2. Geopolitical Risks and Global Uncertainty
Geopolitical risks, such as tensions in Eastern Europe, trade disputes, and potential conflicts in the Middle East, will continue to drive gold prices. As global instability persists, gold is likely to remain a go-to asset for risk-averse investors, further contributing to its price volatility.
3. Digital Gold and Changing Investor Sentiment
The rise of digital gold and increased interest in gold-backed cryptocurrencies may also influence gold’s price dynamics in the future. As more investors turn to alternative forms of gold investment, the relationship between traditional gold prices and digital gold assets could lead to new price patterns and volatility.
Conclusion
Gold’s price volatility is driven by a complex web of factors, including global economic events, market speculation, central bank policies, inflation, and geopolitical risks. While this volatility can be unsettling for some investors, it also presents opportunities for those who understand the dynamics of the market. By monitoring key factors that influence gold’s price movements and using strategies such as buying during market dips and diversifying portfolios, investors can navigate the ups and downs of the gold market and potentially benefit from gold’s volatility in the years to come.