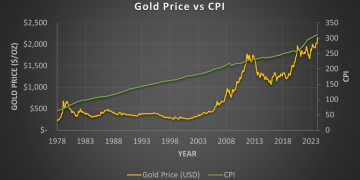
Gold has always been a safe-haven asset, revered for its ability to protect wealth during times of economic turmoil. However, the meteoric rise in gold prices in 2025 has left many investors, analysts, and market observers wondering what exactly is behind this surge. While gold has historically responded to geopolitical instability, inflation, and economic uncertainty, the current market dynamics are unique. This article will break down the key factors driving gold’s price surge in 2025, from geopolitical instability to central bank actions, supply chain disruptions, and future price forecasts based on market trends.
Breakdown of Current Market Conditions: Geopolitical Instability and Central Bank Actions
Gold’s price surge in 2025 is deeply rooted in the current geopolitical and economic environment. The last few years have been marked by unprecedented global instability, with several factors converging to create an environment in which gold is once again seen as a primary asset for risk-averse investors.
Geopolitical Instability: A Key Factor in Gold’s Price Surge
Geopolitical tensions around the world are one of the most significant contributors to gold’s rise in 2025. Conflicts, sanctions, and political uncertainty have sent shockwaves through global markets, pushing investors to seek the safety and security that gold offers. From trade wars to regional conflicts, the global geopolitical landscape is more unstable than ever before.
In particular, the ongoing geopolitical tensions between major powers—such as the U.S.-China relations, the war in Ukraine, and instability in the Middle East—have amplified gold’s appeal. As these tensions continue, many investors have been moving their capital into gold as a hedge against potential market volatility, currency devaluation, and geopolitical crises.
Additionally, the growing concerns about energy security, food shortages, and mass migration due to global political instability have further driven demand for gold. As governments scramble to deal with these challenges, gold remains a stable asset that can weather the storm of global crises.
Central Bank Actions and the Impact on Gold Prices
Central banks around the world have also played a crucial role in driving gold prices higher. With global inflation rates hitting multi-decade highs, many central banks have been aggressively lowering interest rates and engaging in expansive monetary policies to stimulate economies. These actions have led to concerns about the long-term sustainability of fiat currencies, prompting investors to turn to gold as a store of value.
In 2025, central banks have maintained accommodative policies despite high inflation, keeping interest rates low and increasing their gold reserves. The European Central Bank (ECB) and the Federal Reserve have both signaled that they will continue to prioritize economic growth, even at the cost of higher inflation, which has made gold even more appealing as a hedge against currency devaluation.
In addition, central banks have been diversifying their reserve portfolios, increasing gold holdings to ensure financial stability in an uncertain global environment. These institutional actions have helped maintain upward pressure on gold prices, reinforcing its status as the asset of choice for both central banks and individual investors.
Analysis of Gold’s Performance Relative to Other Commodities
One of the most striking features of the 2025 gold market is how gold’s performance compares to other commodities. While gold has always been viewed as a unique asset, the price movements of other commodities—such as oil, silver, and copper—are also important factors in understanding gold’s surge.
Oil and Gold: A Historical Relationship
Oil and gold have long had a close relationship, particularly during periods of inflation. As oil prices rise, so do the costs of goods and services, which can lead to higher inflation. This, in turn, typically boosts gold prices as investors look for assets that can retain value during inflationary periods. In 2025, the price of oil has been volatile, primarily due to geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions. As oil prices have surged, so too has demand for gold, with many investors seeking to protect their wealth from the knock-on effects of rising energy prices.
Silver, Copper, and Industrial Commodities
Gold’s performance in relation to industrial commodities like silver and copper has also been noteworthy. While silver is often seen as a “poor man’s gold” due to its lower price point, its price movements tend to follow gold’s to some extent. However, silver’s volatility and its status as an industrial metal mean that its price can also be influenced by factors beyond just inflation or currency devaluation, such as supply-demand dynamics in various industries.
Copper, another industrial commodity, has faced significant price fluctuations in 2025, partly due to supply chain issues and reduced demand from key manufacturing sectors in China. Gold, by contrast, has performed relatively steadily, with its demand driven more by economic uncertainty and risk aversion rather than industrial use. This has further highlighted the safe-haven appeal of gold compared to more volatile commodities.
The Role of Precious Metals in Portfolio Diversification
Given these dynamics, gold has outperformed many other commodities in 2025 as a means of portfolio diversification. Unlike oil or industrial metals, gold is not directly tied to supply chain disruptions or manufacturing activity, which makes it a more stable investment during times of market turmoil. This has led to a surge in demand for gold among institutional investors, hedge funds, and individual investors looking for a safe haven amid broader market volatility.

The Role of Supply Chain Disruptions in Gold Pricing
In addition to the geopolitical and central bank-driven factors, supply chain disruptions have also played a significant role in gold pricing in 2025. The global supply chain has been under immense pressure in recent years, particularly due to the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent logistical bottlenecks. These disruptions have impacted the production and distribution of many goods, including precious metals.
Mining and Refining Challenges
Gold production has faced its own set of challenges, with mining operations in key regions experiencing slowdowns, worker shortages, and escalating operational costs. In particular, gold mining operations in countries like South Africa, which has some of the world’s oldest and most labor-intensive gold mines, have struggled to maintain output levels. Additionally, environmental regulations and geopolitical instability in major gold-producing regions have hindered supply growth.
As demand for gold has continued to rise, these supply constraints have pushed gold prices even higher. The global mining supply is unable to keep up with demand, further driving the price of gold upward. With many investors seeking to acquire physical gold in the form of bullion, coins, or jewelry, the limited supply of gold has only intensified the upward pressure on its price.
Impact of Increased Demand for Physical Gold
In 2025, there has been a noticeable surge in demand for physical gold, as investors rush to secure tangible assets amid economic uncertainty. This has placed additional strain on the supply chain, particularly in terms of gold refining and distribution. The high demand for gold in its physical form, coupled with supply chain disruptions, has further fueled the price surge.
Future Price Forecasts Based on Market Data and Trends
Looking ahead, many analysts are projecting that gold prices could continue their upward trajectory in 2025, although the pace of growth may slow down depending on various factors such as central bank policy, geopolitical stability, and inflation rates.
Analysts’ Forecasts for Gold in 2025 and Beyond
Several market analysts believe that gold could break past the $2,000 per ounce mark in 2025, with some forecasting even higher prices if geopolitical tensions escalate or if inflation remains persistently high. The continued expansionary monetary policies from central banks and the ongoing risks posed by geopolitical instability could support gold’s upward movement throughout the year.
However, there are also analysts who caution that gold’s price may face resistance if central banks begin to tighten monetary policies or if inflation starts to subside. These analysts argue that a shift in interest rate policies or a stabilization in global supply chains could lead to a correction in gold prices.
Long-Term Outlook for Gold Prices
In the long term, gold’s role as a store of value is expected to remain intact, with many experts predicting that it will continue to be an essential asset in investor portfolios, particularly during times of economic uncertainty. The primary drivers of gold’s price in the future will likely be geopolitical risks, central bank policies, and inflationary pressures.
Conclusion
Gold’s price surge in 2025 is a result of a confluence of factors, including geopolitical instability, central bank actions, supply chain disruptions, and the role of gold as a safe-haven asset during periods of market turmoil. While its performance has outpaced many other commodities, the price of gold remains vulnerable to changes in global economic conditions. Investors will need to monitor geopolitical developments, central bank policies, and supply chain challenges to better understand how these factors will continue to drive gold prices. As always, gold remains a cornerstone of portfolio diversification, providing a stable store of value in uncertain times.